AI
AI only needs to listen to the sound of keystrokes to predict the content, achieving an accuracy rate of up to 95%
A group of researchers from Cornell University (Ithaca, New York) has utilized AI to accurately predict inputted content solely by listening to the sound of keystrokes.
Accordingly, the research team used a database of keyboard typing sounds to train the Artificial Intelligence. Through this method, the AI can predict the content being typed on the keyboard with an accuracy of up to 95%. This accuracy only drops to 93% when using Zoom to train the system.
However, the training approach of the research team from Cornell University still has several limitations. For example, the AI’s predictive ability cannot be immediately applied to any random type of keyboard.
In other words, the AI needs some time to ‘familiarize’ itself with each specific type of keyboard, as each keyboard typing sound is used as a reference for the AI to predict characters during the training process. The actual training of the AI model can be conducted on the spot using a microphone, or even remotely through applications like Zoom to record the keyboard typing sounds.
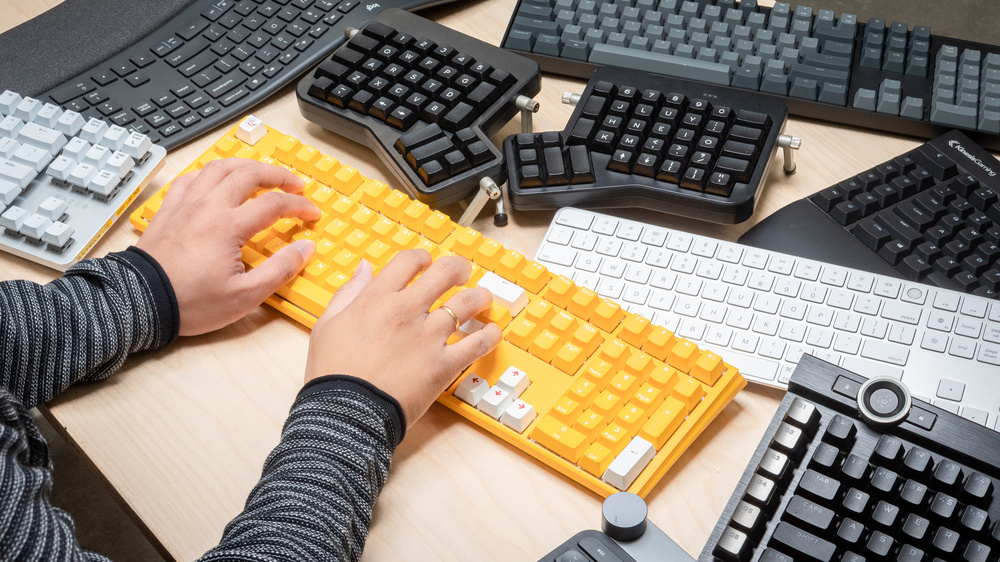

It is known that the research team utilized a MacBook Pro to demonstrate the AI’s capability in predicting content. They pressed 36 different keys, with each key being pressed 25 times. This formed the basis for the AI model to recognize which character was being typed, corresponding to the sound of keyboard typing. Despite the minor variations in the audio waveform produced for each keystroke, the AI accurately identified each key astonishingly.
Of course, employing the AI model for malicious purposes (such as data theft) is not a sound idea, as there still exist numerous vulnerabilities.
Certainly, there have been concerns about the potential misuse of the AI model for nefarious purposes (like data theft). Nevertheless, this type of attack is not without weaknesses, according to the research team.
For example, simply altering the typing style is enough to diminish the accuracy of the AI’s content prediction. Using a gentle touch typing style, the AI’s accuracy in recognizing content drops from 64% to 40%. Additionally, users can employ software to introduce noise as input interference (using white noise) or introduce extra keystrokes to ‘confuse’ the AI.
Different keyboard types themselves also bring about varying risks in terms of data theft by AI. For instance, the accuracy of AI’s data prediction tends to be higher when users utilize mechanical keyboards, which generate louder typing sounds compared to regular keyboards. However, even when using membrane keyboards (which use a rubber dome instead of individual switches under each key), enough sound is produced to train the AI model.
As a result, the most effective way to mitigate this type of attack is to implement a software-based solution rather than switching from a ‘noisy’ keyboard to a quieter one.
According to Tomshardware
AI
Elon Musk’s super AI Grok was created within two months.
The development team of xAI stated that Grok was trained for two months using data from the X platform.
“Grok is still in the early testing phase, and it is the best product we could produce after two months of training,” xAI wrote in the Grok launch announcement on November 5th.
This is one of the AI systems that has been trained in the shortest amount of time. Previously, OpenAI took several years to build large language models (LLMs) before unveiling ChatGPT in November 2022.
xAI also mentioned that Grok utilizes a large language model called Grok-1, which was developed based on the Grok-0 prototype with 33 billion parameters. Grok-0 was built shortly after the company was founded by Elon Musk in July of this year.
With a total time of approximately four months, the company asserts that Grok-1 surpasses popular models like GPT-3.5, which is used for ChatGPT. In scoring benchmarks on mathematical and theoretical standards such as GSM8k, MMLU, and HumanEval, xAI’s model outperforms LLaMa 2 70B, Inflection-1, and GPT-3.5.
For example, in a math problem-solving test based on this year’s Hungarian National High School Math Competition, Grok-1 achieved a score of 59%, higher than GPT-3.5’s score of 41% and only slightly below GPT-4 (68%).
According to xAI, the distinguishing feature of Grok is its “real-time world knowledge” through the X platform. It also claims to answer challenging questions that most other AI systems would reject.

On the launch day, Musk also demonstrated this by asking the question, “the steps to make cocaine.” The chatbot immediately listed the process, although it later clarified that it was just joking.
This is the first product of Musk’s xAI startup, which brings together employees from DeepMind, OpenAI, Google Research, Microsoft Research, Tesla, and researchers from the University of Toronto. Musk is also a co-founder of OpenAI, the organization behind ChatGPT, established in 2015. He later left the company due to disagreements over control. During his departure, he declared his intention to compete for talent from the company while also cutting off the previously promised $1 billion in funding.
Read more: Google, Meta, Microsoft, OpenAI… agree with voluntary measures to protect AI.
AI
AI generation – a new battleground in phone chip design.
Smartphone and mobile chip manufacturers are participating in the wave of AI generation to bring this technology to phones in the near future.
AI generation has exploded over the past year, with a range of applications being released to generate text, images, music, and even versatile assistants. Smartphone and semiconductor companies are also building the latest hardware to not miss out on the wave. Leading the way is Google’s Pixel 8, while Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 processor is also set to be launched in the coming days.
The latest signs indicate that phone manufacturers are welcoming AI generation from Google. The Pixel 8 series is the first set of smartphones capable of operating and processing Google’s Foundation Models for AI generation directly on the device without the need for an internet connection. The company stated that the models on the Pixel 8 reduce many dependencies on cloud services, providing increased security and reliability as data is not readily available.
This has become a reality thanks to the Tensor G3 chip, with the Tensor (TPU) processor significantly improving over last year. The company usually keeps the operation of the AI chip secret but has revealed some information, such as the Pixel 8 having double the number of on-device machine learning models compared to the Pixel 6. The AI generation on the Pixel 8 also has the ability to compute 150 times faster than the largest model of the Pixel 7.
Google is not the only phone manufacturer applying AI generation at the hardware level. Earlier this month, Samsung announced the development of the Exynos 2400 chipset with AI computing performance increased by 14.7 times compared to the 2200 series. They are also developing AI tools for their new phone line using the 2400 chip, allowing users to run text-to-image applications directly on the device without an internet connection.
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon chip is the heart of many leading Android smartphones globally, which raises expectations for the AI generation capabilities on the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 model.
Earlier this year, Qualcomm demonstrated a text-to-image application called Stable Diffusion running on a device using Snapdragon 8 Gen 2. This indicates that image generation support could be a new feature on the Gen 3 chipset, especially since Samsung’s Exynos 2400 also has a similar capability.
Qualcomm Senior Director Karl Whealton stated that upcoming devices can “do almost anything you want” if their hardware is powerful, efficient, and flexible enough. He mentioned that people often consider specific AI generation-related features and question whether the existing hardware can handle them, emphasizing that Qualcomm’s available chipsets are powerful and flexible enough to meet user needs.
Some smartphones with 24 GB of RAM have also been launched this year, signaling their potential for utilizing AI generation models. “I won’t name device manufacturers, but large RAM capacity brings many benefits, including performance improvement. The understanding capability of AI models is often related to the size of the training model,” Whealton said.
AI models are typically loaded and continuously reside in RAM, as regular flash memory would significantly increase application loading times.
“People want to achieve a rate of 10-40 tokens per second. That ensures good results, providing almost human-like conversations. This speed can only be achieved when the model is in RAM, which is why RAM capacity is crucial,” he added.

However, this does not mean that smartphones with low RAM will be left behind.
“On-device AI generation will not set a minimum RAM requirement, but RAM capacity will be proportional to enhanced functionality. Phones with low RAM will not be left out of the game, but the results from AI generation will be significantly better with devices that have larger RAM capacity,” commented Director Whealton.
Qualcomm’s Communications Director, Sascha Segan, proposed a hybrid approach for smartphones that cannot accommodate large AI models on the device. They can host smaller models and allow processing on the device, then compare and validate the results with the larger cloud-based model. Many AI models are also being scaled down or quantized to run on mid-range and older phones.
According to experts, AI generation models will play an increasingly important role in upcoming mobile devices. Currently, most phones rely on the cloud, but on-device processing will be the key to expanding security and operational features. This requires more powerful chips, more memory, and smarter AI compression technology.
AI
AI can diagnose someone with diabetes in 10 seconds through their voice.
Medical researchers in Canada have trained artificial intelligence (AI) to accurately diagnose type 2 diabetes in just 6 to 10 seconds, using the patient’s voice.
According to the Daily Mail, a research team at Klick Labs in the United States has achieved this breakthrough after their AI machine learning model identified 14 distinct audio characteristics between individuals without diabetes and those with type 2 diabetes.
The AI focused on a set of voice features, including subtle changes in pitch and intensity that are imperceptible to the human ear. This data was then combined with basic health information, including age, gender, height, and weight of the study participants.
The researchers found that gender played a determinant role: the AI could diagnose the disease with an accuracy rate of 89% for women, slightly lower at 86% for men.
This AI model holds the promise of significantly reducing the cost of medical check-ups. The research team stated that the Klick Labs model would be more accurate when additional data such as age and body mass index (BMI) of the patients are incorporated.
Mr. Yan Fossat, Deputy Director of Klick Labs and the lead researcher of this model, is confident that their voice technology product has significant potential in identifying type 2 diabetes and other health conditions.
Professor Fossat also teaches at the Ontario Tech University, specializing in mathematical modeling and computational science for digital health.
He hopes that Klick’s non-invasive and accessible AI diagnostic method can create opportunities for disease diagnosis through a simple mobile application. This would help identify and support millions of individuals with undiagnosed type 2 diabetes who may not have access to screening clinics.
He also expressed his hope to expand this new research to other healthcare areas such as prediabetes, women’s health, and hypertension.
-

 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoMusk aims to create a super AI to rival ChatGPT
-

 Mobile2 years ago
Mobile2 years agoProduction issue with iPhone 15 display raises concerns among users
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoSurprisingly, a single YouTube video has the potential to cause serious harm to Google Pixel’s top-of-the-line smartphone
-

 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUpon its debut, Google’s chatbot Bard dealt a cold blow to its very creator.
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoCS:GO Breaks Records with Surging Gamer Engagement and Increased Spending
-

 Crypto1 year ago
Crypto1 year agoExplore in detail about Web 3
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoHuawei has demonstrated to the world that making electric cars is as easy as assembling smartphones
-

 Entertainment1 year ago
Entertainment1 year agoRumors have been circulating about a live-action film about GTA, the creator of the series spoke out to confirm one thing.